Membrane Structure
The cell has to have boundaries that keep
all of its' components close together. But it has to be constructed in
such a way so that it could regulate what and when materials can come in and
leave the cell. It must also be able to survive a watery environment
The cell membrane has both a polar end and
a nonpolar end. The cell membrane is called the phospholipid membrane
because it has a non-polar lipid end and a polar phosphate end. The polar
phosphate is called hydrophillic because it will align itself automatically so
that it touches the polar water molecule. It seeks water. The
non-polar lipid end of the phospholipid molecule consists of 2 strands of fatty
acids that extend from the phosphate head. The fatty acid tail is said to
be hydrophobic because it will align itself in a direction away from water.
Most lipids are hydrophobic . This is why water and vegetable oil will not
mix. 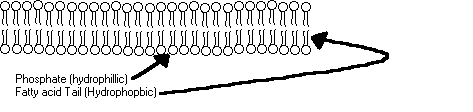 There are more components in the
phospholipid membrane than just phospholipids. There are proteins in the
membrane. The type of protein depends the function of that protein for
that cell. There are 3 types of membrane proteins. These include
integral proteins, channel (pore) proteins and surface proteins. Along
with those proteins are molecules of cholesterol the function of which is
structural integrity of the membrane. The membrane is said to be fluid, in
that the particles are able to move around a little within the structure of the
membrane. The proteins and cholesterol molecules are placed in the
membrane in a random fashion. It is like a mosaic tile pattern on a wall
or floor. It is because of these two factors that the membrane is said to
be a fluid mosaic.
There are more components in the
phospholipid membrane than just phospholipids. There are proteins in the
membrane. The type of protein depends the function of that protein for
that cell. There are 3 types of membrane proteins. These include
integral proteins, channel (pore) proteins and surface proteins. Along
with those proteins are molecules of cholesterol the function of which is
structural integrity of the membrane. The membrane is said to be fluid, in
that the particles are able to move around a little within the structure of the
membrane. The proteins and cholesterol molecules are placed in the
membrane in a random fashion. It is like a mosaic tile pattern on a wall
or floor. It is because of these two factors that the membrane is said to
be a fluid mosaic.
Back
Next
 There are more components in the
phospholipid membrane than just phospholipids. There are proteins in the
membrane. The type of protein depends the function of that protein for
that cell. There are 3 types of membrane proteins. These include
integral proteins, channel (pore) proteins and surface proteins. Along
with those proteins are molecules of cholesterol the function of which is
structural integrity of the membrane. The membrane is said to be fluid, in
that the particles are able to move around a little within the structure of the
membrane. The proteins and cholesterol molecules are placed in the
membrane in a random fashion. It is like a mosaic tile pattern on a wall
or floor. It is because of these two factors that the membrane is said to
be a fluid mosaic.
There are more components in the
phospholipid membrane than just phospholipids. There are proteins in the
membrane. The type of protein depends the function of that protein for
that cell. There are 3 types of membrane proteins. These include
integral proteins, channel (pore) proteins and surface proteins. Along
with those proteins are molecules of cholesterol the function of which is
structural integrity of the membrane. The membrane is said to be fluid, in
that the particles are able to move around a little within the structure of the
membrane. The proteins and cholesterol molecules are placed in the
membrane in a random fashion. It is like a mosaic tile pattern on a wall
or floor. It is because of these two factors that the membrane is said to
be a fluid mosaic.